Online Help Desk

![]() Online Help Desk
Online Help Desk
Free help – right here, right now!
The PC Pitstop team have complied a list of handy articles below to help you through some of the most common computer hiccups. Bookmark this page for speedy access! Alternatively, Remote Support is available and is great for jobs requiring technical expertise but do not require an onsite call-out. For regular help desk updates subscribe to the PC Pitstop Blog, the e-newsletter, or follow us on facebook.
Helpdesk Articles
Computing Acronyms
MB = Motherboard, the main part of a computer which all other parts plug into, often the most expensive part of a computer to replace.
HDD = Hard Drive Disk or Hard Drive, used to store data on a computer, size measured in gigabytes or terabytes.
MSE = Microsoft Security Essentials (Anti-Virus)
RAM = Random Access Memory (Necessary for computer to function, more RAM = More speed, comes in 512MB, 1GB, 2GB etc.)
DDR1, DDR2, DDR3 = Various types of RAM (memory)
MB = Megabyte, unit of measurement for hard drive or RAM size
GB = Gigabyte, unit of measurement for hard drive or RAM size, 1GB = 1000MB
TB = Terabyte, unit of measurement for Hard Drive size, 1TB = 1000GB
CPU = Central Processing Unit or Processor, comes in two brands either Intel or AMD. Known as the “brain” of the computer, essential for computer to run, faster processor = faster computer.
Dual Core/Quad Core = Different types of processor, Quad core mainly used by gamers and hardcore users.
i3, i5, i7 = Newer types of Intel Processors, i5 is Dual Core, i7 is Quad Core
Video Card/Graphics Card = Used to send the signal from the computer to the monitor, can be either part of the motherboard or a separate card, the more powerful the video card the more graphics intensive games you can play.
VGA or D-SUB = The most basic plug for connecting a computer to a monitor, the two plugs are often blue coloured.
DVI = A higher quality computer to monitor connection, wider than VGA plugs and often white in colour.
HDMI = High Definition Multimedia Interface, the newest kind of computer to monitor cable, High definition quality, also carries audio, is usually used to plug a computer into Plasma or LCD screens and is used in Game Consoles and Blu Ray players.
DVD Reader/CD Burner = Will play DVDs and burn CDs
DVD Writer = Will burn and play DVDs and CDs
CD Writer = Will burn and play CDs not DVDs
Blu Ray Drive = Will burn and play CDs and DVDs will only play Blu Ray Discs Blu Ray Writer = Will burn and play CDs, DVDs and Blu Ray Discs
PCI = Connection on motherboard for connection Sound Cards, USB cards, dial up modems etc.
PCI Express = Connection on motherboard for Video Cards
PCIMIA or ExpressCard Slot = Slot on the side of laptops for connecting an expansion card, usually wireless or extra USB ports.
AGP = Accelerated Graphics Port, connection on older motherboards for graphics cards
SATA = Newer connection on motherboards for connecting hard drives and DVD or Blu Ray Drives
IDE or PATA = Older connection on motherboards for connecting hard drives or disc drives, wide flat ribbon cable.
USB = Universal Serial Bus, used to connect devices such as iPods, Cameras, Printers, Keyboards etc. to computers, is either USB 1.0 (Older computers), USB 2.0 (modern computers) or USB 3.0 (newest computers)
Serial/Parallel = Older connection for printers, modems etc.
Ethernet = Cable used to connect computer to a network or modem for broadband, looks like an oversized phone cable
ADSL = Home broadband through the phone line, currently the fastest and cheapest way to access the internet
ADSL2+ = A faster version of ADSL
Wireless = Used to connect computers to a modem for broadband
Wireless Broadband = Using a USB Stick to connect to a mobile network (Telstra, Optus, Dodo etc.) to access the internet, is slower and more expensive than ADSL but good for travelers. Please note that when selling wireless broadband you explain to the customer there is no guarantee that it will work where they want it to due to it needing mobile reception to work and there are NO refunds. It is essentially the same as buying a mobile phone. Note: Wireless is built into most modern laptops, wireless broadband MUST be purchased separately they are NOT the same thing.
Connection Guide
- Most computer plugs are colour coded and will only plug in one way. Please pay special attention to the way they do plug in so as not to damage them by force.
- USB plugs can go into any USB socket.
- If you have two blue video sockets on the back of your computer, the horizontal plug (PCI-E Video Card) will take precedence over the vertical plug (onboard video).
- Speakers connect to the green socket.
- Microphone connects to the pink socket.
- Your internet will usually connect to the large square hole that resembles a large telephone socket called “Ethernet”.
- If you have dialup internet, you will have a modem with a small telephone plug.
Cleaning Your Computer
General Cleaning Tips:
- Wipe down the outside of your computer at least once a week to avoid dust collecting and working its way into your computer’s vital parts.
- Do not smoke by your computer.
- Do not put computer near any source of heat or on the ground, preferably keep it on a desk/table if possible. This will also avoid the computer been kicked or knocked which can damage vital parts such as the Hard Drive.
- Open a window occasionally to recycle the air, but do not leave a window open near the machine for long periods of time – especially on the coast where corrosion can also wreak havoc on computers.
- Make sure your computer room is cleaned regularly. A room that is well ventilated and free of animal hair will be less likely to allow dust to build up on or inside your machine.
- Always turn off your computer or computer components before cleaning.
- Never spray or squirt any type of liquid directly onto any computer component. If a spray is needed, spray onto a cloth and then rub down the component.
- For keyboard spills turn the computer off immediately, and then quickly flip the keyboard to prevent the substance from penetrating circuits. While still upside down, use a cloth to help clean out what can be reached. Leave upside down until dry. If a keyboard does not work after trying it again later it is recommended that it be replaced.
Backing Up


Backing up your files is basically copying all your important files to an external device that can be easily taken off-site each day for security measures in business or easily accessible during an evacuation – keeping your precious data and memories safe and saving you time, money and tears.
How to do a basic backup:
1. Insert/plug-in your External Hard Drive (or Flash Drive)
2. Go to the folder or location of the files you want to backup
3. To select all the files in that location, click the “edit” menu at the top of the screen, then click on “Select All” from the list.
4. You will now notice all the files in the folder are highlighted, this is telling the computer that you have selected these files
5. Now use your “right” mouse button and click on one of the highlighted files
6. You will see a little menu appear, run the mouse over the “Send To” item then left click on “Backup Disk” or “(E:) disk” or similar.
7. Your files will now copy/backup to the external device.
Devices
External Hard Drive: Can be purchased in varying sizes. Those with a large amount of data or photos should consider a 1 or 2TB HDD. These can be set to ‘automate’ quite easily, to backup anything you have changed at a certain time each day.
Flash Drive: Also called thumb drives or memory sticks, these also come in various sizes, although a lot smaller. They become quite expensive past the 8GB mark, where it would be more economical to purchase an External HDD. Flash drives are still great for conveniently transporting a few files from one location to another.
Disk Defrag Procedures
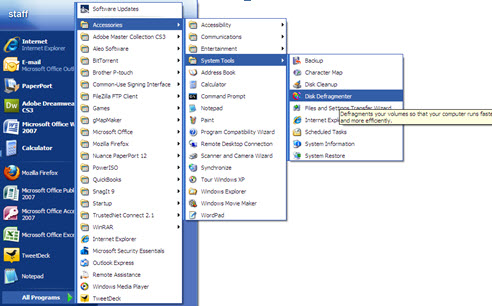
Defragmentation is a process that reduces the amount of fragmentation in file systems. It organises the contents of your hard drive to store files in the smallest possible number of regions (fragments), attempting to create larger regions of free space to allow the hard drive to ‘read’ the data much more quickly.
- Start Menu – All Programs – Accessories – System Tools
- Disk Defragmenter (click to open program) * * ‘Defragment’ – Defragmenting process will take awhile, once Defrag is complete a window will pop up informing you, just simply close the program.
Batteries & Charges

Your laptop battery charges whenever your computer is plugged into external power through an AC Adapter, an optional power adapter, or an optional docking device. The battery charges whether the computer is off or in use, but it charges faster when the computer is off.
However, charging may take longer if a battery is new, has been unused for 2 weeks or more, or is much warmer or cooler than room temperature.

To prolong battery life and optimize the accuracy of battery charge displays, follow these recommendations:
- If you are charging a new battery, charge it for a full 12 hours before turning on the computer.
- Charge the battery until the battery light turns off (If the computer is on while the battery is charging, the battery meter in the notification area may show 100 percent charge before the battery is fully charged.)
- Allow the battery to discharge below 5 percent of a full charge through normal use before charging it.
- If the battery has been unused for one month or more, calibrate the battery instead of simply charging it.
- DO NOT drop, open, short circuit, burn or allow the battery to get wet.
Laptop Safety Tips
Safely using your laptop will help ensure that your laptop works properly and you don’t get injured. Improper use or not being aware of safety issues can cause your laptop irreparable damage. These safety tips should be added to your weekly laptop maintenance routine and will help you stay productive and safe no matter where you are working.
- Shut It Down – Unlike a desktop computer a laptop computer needs to be shut down when not in use to prevent overheating.
- Overheating is very dangerous to the internal systems. If the drive inside your computer gets too hot it is very possible to start losing data and very hard to get it all back.
To lessen the chances of overheating (or burning your lap!), the following products available from PC Pitstop can help:
Laptop Coolers (From $28.00) – A USB powered device which sits under your laptop cooling for superior heat dissipation.
Laptop Risers (From $19.50) – A non-skid platform that can be used in conjunction with a cooler or on its own to promote airflow around the base of the laptop, also offering greater ergonomic comfort, positioning and viewing.


- Checking the Fan – Overheating problems can also be caused by the laptop fan not working properly. Always check the laptop manufacturer’s online support and your warranty information.
- Vent Maintenance – Part of your weekly routine should be to inspect and clean the air vents in your laptop. Forced air dusters can be used to keep the air vents clean and free from debris. It’s important to know that you should never push anything into the air vents
- Adjusting Power Settings – Adjusting your power options will help your laptop from heating up when not in use even if for short periods of time. You can set your hard drive and display to turn off after a set time period. Another option is to set the laptop to go into standby or hibernate mode.
- Before You Pack It Up – Make sure that you before you put your laptop into its carrying bag that it is shut down. A notebook that has been left on can melt. When enclosed in a notebook bag there is no air circulation and the results can be worse than melting. Don’t find out the hard way and just be sure to turn off your laptop.
- Soft Spots – It’s a wise idea not to use any soft material as a buffer between you and your laptop. Always operate your laptop on a hard surface, preferably one that allows ventilation. Soft materials can block the airflow vents and cause it to overheat. If it is not possible to avoid using a soft surface, an optional heat sink base should be used to maintain cooling.
- Unplug Accessories – Whenever your laptop will not be in use, even for short periods of time remember to unplug any accessories. Not only do they use power but they could cause the laptop to overheat. It’s especially important to unplug any accessories before packing your laptop in its carrying case. While you may believe it will make it quicker to use, it could damage your laptop, the accessory and/or your laptop bag.
Cables and Connections
HDD IDE Cable: Integrated Drive Electronics, a ribbon cable that connects an older style hard drive to the motherboard inside the computer.
SATA Male to SATA Male, 90-degree ends, 50cm: Supports data transfer speeds up to 3.0 Gbps. Connects SATA 150 and SATA 300 controllers to devices
Serial ATA Data Cable: is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives.
Molex power cable 5.25M to 2 x 5.25M, 20cm: is the vernacular term for a two-piece pin and socket interconnection, most frequently disk drive connectors.
Serial ATA (SATA) –> Molex power adapter: is a computer bus technology primarily designed for transfer of data to and from a hard disk.
3 pins Power Cord: are devices for removable connecting electrically operated devices to the power supply. An electric plug connects mechanically to a matching socket. Usually plugs are movable connectors, and sockets are fixed to equipment.
Power Cable – 250V:
VIDEO VGA cable, M-M, 1.8m: The most basic plug for connecting a computer to a monitor.
DVI-I Male to VGA Female video adapter: VGA connectors are found on many video cards, computer monitors, and some high definition television sets.
HDMI Female to DVI-D 24+1 Male adapter:
HDMI Male to DVI-D 24+1 Female adapter:
VGA Extension cable, M-F, 3m:
HDMI Cable M-M 2m: USB USB A-A extension cable, translucent silver, 0.3m:
USB A-B cable, translucent silver, 2m:
USB 3.0 A-A extension cable, blue:
USB 3.0 A-B cable, blue:
Ethernet (Internet) Cable:
Avoiding Viruses and Scams
PC Pitstop sees all manner of viruses and software ‘bugs’ every day from a huge range of different sources. It is near impossible to keep up with speed at which new viruses or scams spread, but common sense tells us where to look.
So it is with this knowledge that we have compiled some basic tips to avoid costly and damaging issues from viruses occurring on your machine:
- Be sure to keep your machine up to date – with the latest patches from Windows Update. These software patches fix bugs and exploits and help to keep your machine secure from the newest viruses.
- Watch your web browsing habits – There are billions of sites on the internet and not all of them are nice. Most of these sites are related to adult content, ‘free’ downloads such as music; software and movies; online flash game websites; and gambling websites such as online poker. If you are going to download or sign-up for something on a website make sure it is a verified safe site beforehand possibly by searching for the name of the site/service on Google.
- Do not open email attachments from people you do not know! This is the leading cause of virus infection and also the way most viruses spread, even if it is not an application in the attachment the file can still be infected or trigger an exploit on your system leading to your system being infected. Only open attachments from known people, and even then use caution.
- Keep your identity safe online – do not give information out to strangers or to random web sites. This includes your name, address, phone number etc… as this information can be used for nefarious purposes such as bank scams or identity theft.
- Avoid pop-ups or banners offering FREE product – most of these lead to malicious web sites or scams. These will usually present you with a window that reads something along the lines of “Your system is infected – Click here to run a FREE virus scan!” Do not click on these, just close the window and ignore them. If you are genuinely concerned about viruses, pop into PC Pitstop for a true virus health check.
- Finally, avoid taking calls from ‘technicians’ claiming that your computer is infected – No-one outside of the person directly in front of your machine can know exactly what is or isn’t wrong with your computer. These tricky scammers will usually ask you to type something into your machine, providing them with remote access, where they can then cause a lot of damage. Hang up on them and never hand over credit card details to someone you don’t trust.
Keep these points in mind for HAPPY HEALTHY COMPUTING!
Beware Spyware
How to keep spyware from tracking your habits – or hijacking your computer.
One-third of Internet users have been spyware afflicted, according to a recent survey by Consumer Reports. “Spyware, without question, is on an exponential rise over the last six months,” says Alfred Huger, senior director of engineering with Symantec Security Response, the maker of Norton security software. Microsoft reports that spyware was the cause of one-third of all computer crashes in the past year. Because it’s so new and still evolving, many computer users don’t understand spyware.
Here’s a quick tutorial to bring you up to date on this insidious problem.
- What is spyware? It’s a broad term for deceptive software that surreptitiously installs itself on a computer via the Web. Once it lurks on your PC or laptop, it allows an outsider to harvest your personal information, which can be used for many purposes. In its most benign form, a kind of spyware known as adware tracks Web surfing or online buying so marketers can send you targeted – and unsolicited – ads. Other spyware may have a more malicious intent, such as stealing passwords or credit-card information. Having a number of unauthorized programs running on your PC at once makes it sluggish, unstable, and, ultimately, more likely to crash.
- How do you know if your computer has been infiltrated with spyware? Unlike viruses, which are often invisible, spyware exhibits a host of signs that ‘take away a user’s ability to control the computer.’ Hijacked home pages, redirected Web searches, and a flood of pop-up ads are common complaints.
- How does spyware sneak on board? Simply clicking on a banner ad can install spyware. Worms, which are self-propagating viruses, can also carry spyware. They search for machines that don’t have up-to-date security patches and install the nasty software. Spyware is also spread by e-mail. Sometimes spyware is secretly bundled with free software you download from the Internet. Sites that offer music-sharing, videos, weather data, games, and screen savers often are paid to distribute adware. When you install the software, you might see a pop-up window that asks you to agree to certain conditions. Most users just click ‘I agree’ without reading the fine print. Often they are authorising the installation of additional data collection and ad serving software that can damage their PCs.
- How do you get rid of spyware? To eliminate it, you must track down every file and completely erase it. That can be tough since spyware hides inside your computer’s operating system, making it difficult to find. Some Internet service providers offer scan-and-removal tools. For extra protection, you should also employ specialty anti-spyware software. Be careful about the programs you choose to ensure they are not spyware disguised as spyware cleaners. Use a well-known program that scans for a regularly updated list of privacy threats. Scan your hard drive at least once a week with two or more anti-spyware programs because each is likely to find files the other overlooks. For files that can’t be deleted, contact PC Pitstop.
- How do you protect your computer in the future? Protection is an ongoing process since spyware makers are constantly creating new threats. First, install a personal firewall and an anti-virus program.
Next, set the computer’s operating system for daily security updates. Also set the Web browser to a medium- or high-security level. For Windows, go to Microsoft’s website for instructions. Windows XP users should install Service Pack 2, which makes it close to impossible for software to be downloaded without your being alerted. - Finally, practice safe surfing. That means downloading only trustworthy software, reading licensing agreements, avoiding banner ads, and deleting spam.
The Virus Eradication Race
Combating viruses is a three way race:
- In the lead are virus writers looking for vulnerabilities and writing viruses to exploit them.
- Coming in second are the anti-virus software vendors looking for ways to detect each new virus as it appears, as well as figure out the correct way to eradicate it when found. Then the vendors are looking to plug the security holes that the viruses exploited in the first place.
- Lastly are people like you and me: hopefully keeping our systems up to date with the latest updates to our anti-malware products as well as the systems and software that have vulnerabilities.
Get Protected! – Some classes of viruses exploit operating system vulnerabilities that are present simply by connecting to the internet. You don’t even have time to download your operating system update, or anti-virus software, before your machine is once again a victim.
Firewalls help – particularly hardware firewalls such as modem/routers. Firewalls understand the difference between certain types of legitimate internet traffic, and types that you’d never need. They block out the unwanted stuff before your computer ever really sees it, or has a chance to be infected by it. The good news here is that all operating systems now either come with a software firewall turned on by default.
The Harsh Reality – All viruses are not created equal – hence all the different terms used to describe them. Some exist merely to propagate, others exist to do damage, and some exist to silently send spam while still others start to blur the line between virus and spyware as they install monitoring or additional vulnerabilities on your system. Some travel by email, others by downloaded applications, and others can travel from unprotected computer to unprotected computer directly through the internet.
No anti-malware tool can protect you from yourself. For example, if you open an email attachment you don’t recognize and run it, you may install a virus before your anti-virus software has a chance to act. If, when downloading a file, you choose to ignore a warning that your anti-virus package or firewall throws up, you’re telling the software that you know better than it does what is or is not safe.
Why? – Ask 10 people and you’ll get 10 different answers: Hackers with too much free time, operating systems that aren’t robust enough, success in the marketplace that makes for a bigger target, and more. Of course it shouldn’t be like this… But what we do know is that it for whatever reason is like this, and will be for the foreseeable future. That’s why, ultimately, you and I are each responsible for keeping our computers safe on the internet.
Giving Reboots the Boot!?
Why Get a Graphics Card?
PC Pitstop research analysed our customers computers and found the following facts regarding computer security:
- 23% of computers have no active security protection.
- 14% of the computers had some sort of high level threat.
- Spyware is the most common malware threat followed by Rogue Security Software.
- Symantech Norton Internet Security provides the best protection accross all requirements



